Many of you find very complicated and tedious to analyze any country’s performance and usually get afraid...
Blog
The Fed’s Senior Loan Officer Opinion Survey (SLOOS) report indicated that demand for all kinds of loans...
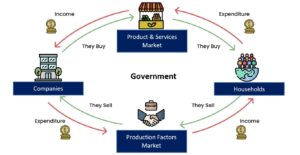
The circular flow of the economy refers to the continuous flow of goods, services, and money between...
The stock market is a platform where investors can buy and sell shares in publicly traded companies....
FX premia and forward premium are two different things, although they are related concepts. Forward premium is...
The forward market is a financial market where participants can enter into contracts to buy or sell...
Currency is a medium of exchange used for buying and selling goods and services. It can be...
The forex (foreign exchange) market is a decentralized global market where currencies are bought and sold. It...
Crude oil prices are volatile for several reasons, including: Overall, the complex and interconnected nature of the...
An FX swap is a foreign exchange transaction that involves two parties exchanging currencies for a set...
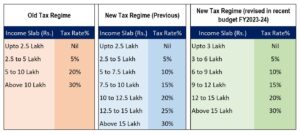
Currently, there are a lot of discussions going on around new tax regime or old tax regime....
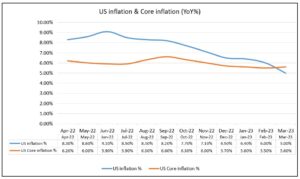
The Bureau of Labour Statistics released the US CPI data for March recently which showed that US...
Saudi Arabia and OPEC+ (Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries) members had announced a 1.16 mbpd (million barrels...
The first RBI’s MPC meeting outcome of FY24 was released on 6th Apr 2023 that surprised the...
India is a developing country and its GDP is growing at around average 7-8% annually. As per...
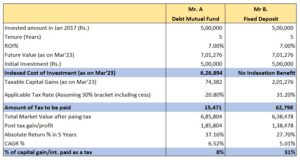
Investing in debt mutual funds was very popular among investors mainly due to indexation benefits. But unfortunately...
Banks are the backbone of financial system that help central bank to control money supply in the...
[ad_1] (Bloomberg) — Amazon.com Inc.’s Prime subscription service hit a new high of 180 million US shoppers...
[ad_1] (Bloomberg) — The US Securities and Exchange Commission was sued by a conservative think tank and...
[ad_1]
Please enable JavaScript if it is disabled in your browser or access the...
[ad_1] (Bloomberg) — The European Union should consider consolidation for telecom operators as a way to improve...
[ad_1] A growing cadre of investors is turning to separately managed accounts, or SMAs, working with advisers...
[ad_1] (Bloomberg) — The recent departure of Citigroup Inc., a perennial top-10 underwriter of municipal debt, from...
[ad_1] UnitedHealth Group Inc. shares soared more than 5 per cent in morning trade on Tuesday after...
[ad_1] Oil prices were largely steady on Tuesday, April 16, after the US announced plans to hit...
[ad_1] Elon Musk is likely to announce its carmaker Tesla’s entry into Indian markets after the billionaire’s...
[ad_1] Gold prices experienced a decline on Tuesday, attributed to mounting expectations of fewer U.S. interest rate...